4.1. LwM2M Client Logic
4.1.1. Overview
This document describes the LwM2M client state machine in Anjay Lite.
It outlines state transitions, error handling, and user-triggered actions
throughout the client lifecycle.
The design supports bootstrap, registration sessions, and manual control via
the anj_core API.
4.1.2. State machine overview
The client state machine includes several operational states, each responsible
for specific tasks and transitions.
Some internal or intermediate states (such as ANJ_CONN_STATUS_INVALID) are
not covered here.
For a full list, refer to the anj_conn_status_t definition in the source
code.
The following diagram illustrates the state transitions, without error handling:

4.1.2.1. Initial
The client always starts in the Initial state.
Validates the presence of LwM2M Security and Server Object instances.
If the Security Object contains only a Bootstrap Server instance (
0/x/1= True), it transitions to Bootstrap.If a regular LwM2M Server instance is found in both Security and Server Objects, it transitions to Registration.
4.1.2.2. Bootstrap
Reads and validates the Bootstrap Server Security instance.
Opens a connection to the LwM2M Bootstrap Server.
Sends a
Bootstrap-Requestmessage.Awaits configuration requests from LwM2M Bootstrap Server.
After receiving
Bootstrap-Finishmessage, closes the connection and transitions to the Registration state.
4.1.2.3. Registration
Reads and validates corresponding Server and Security Object instances.
Opens a connection to the LwM2M Server.
Sends a
Registerrequest.After receiving a valid response, transitions to Registration Session.
When a new registration session starts, clears all existing observations and pending send requests.
4.1.2.4. Registration Session
Handles incoming server requests.
- Schedules
Updatemessages according to the following formula: MAX(lifetime/2,lifetime - MAX_TRANSMIT_WAIT)
where:
MAX_TRANSMIT_WAITis a CoAP-defined transmission parameter that represents the maximum expected time to complete a confirmable message exchange. Check the CoAP specification for more details.If
lifetime(/1/x/1) equals 0, timeout is infinite and noUpdateis sent.If lifetime changes, recalculates the timeout and sends an immediate
Update.If list of objects or object instances changes, sends an immediate
Update.
- Schedules
Handles
NotificationandLwM2M Sendmessages.If queue mode is enabled, transitions to Queue Mode state after the timeout expires. Stage transition is followed by connection closure.
The LwM2M Server may enforce transitions:
to Suspend Mode via resource
/1/x/4to Bootstrap via resource
/1/x/9In both cases, the client first sends
Deregisterand closes the connection.
Note
LwM2M allows only one message exchange at a time.
Large payloads may block other messages.
To avoid blocking during FOTA, use Pull mode instead of Push,
as Pull mode uses a separate connection, avoiding interference with other
operations such as `Update` messages or notifications.
4.1.2.5. Queue Mode
Ignores inbound requests but continues evaluating whether to send
Update,Send, orNotificationmessages.When outbound communication is needed, re-establishes the connection and transitions back to Registration session.
See Queue Mode for more details.
4.1.2.6. Suspend Mode
No operations are performed during suspend mode.
After the Disable Timeout period (resource
/1/x/5) expires, automatically transitions to Initial.Anjay Lite doesn’t yet support buffering notifications while suspended.
Note
Suspend mode is typically less efficient than queue mode, as it requires re-registration afterward.
4.1.3. Error handling logic
The following diagram shows how Anjay Lite handles errors:

Errors are grouped by state, each with its own handling logic.
State / Phase |
Error Types / Additional Information |
Handling Logic |
|---|---|---|
Initial |
Missing or invalid Security and Server Object instances |
Transition to Failure |
Bootstrap |
|
|
Registration |
|
|
Registration Session |
|
Connection closes and re-registration is attempted |
Suspend Mode |
Only closes connection |
Connection closure failure doesn’t change state |
Failure |
Triggered from Initial, Bootstrap or Registration states after retries exhaustion |
Client remains in Failure state until user initiates recovery via
|
4.1.4. User-controlled client management
The anj_core API lets you manage the client lifecycle and force state
transitions.
The client cannot exit the Failure state without explicit user intervention.
The following diagram illustrates the user-controlled client management logic:
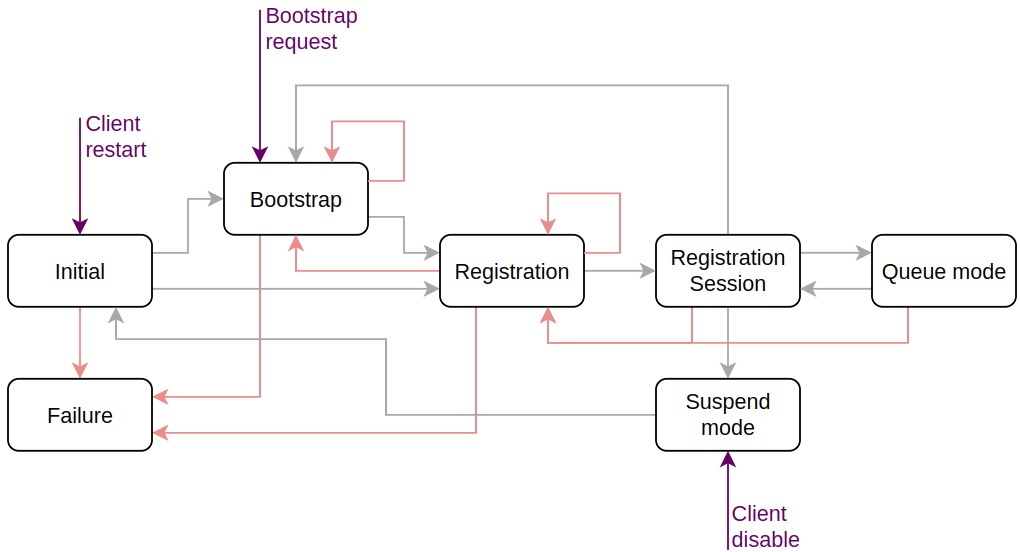
API function |
Description |
|---|---|
|
Forces transition to Initial. |
|
Transitions to Bootstrap unless already bootstrapping. This is the only restriction for forced transitions. |
|
Transitions to Suspend Mode:
|
Note
Transitions triggered by the anj_core API start with a Deregister
message (if the client is registered), followed by closing the connection.
4.1.5. Additional notes
Network configurations are set via
anj_configuration_t.net_socket_cfg.State transitions involving connection closures typically reset the network context, except transitions from Registration Session into either Queue Mode or Suspend Mode.
All requests follow the CoAP specification and support Block-Wise Transfers. Default transaction parameters can be modified via
anj_configuration_t.udp_tx_paramsandanj_configuration_t.exchange_request_timeout_ms.The client supports exactly one LwM2M Bootstrap Server and one regular LwM2M Server instance.
The
anj_core_ongoing_operation()function ensures safe access to objects that might currently be involved in active client operations. Always check its return value to avoid conflicts during concurrent modifications.